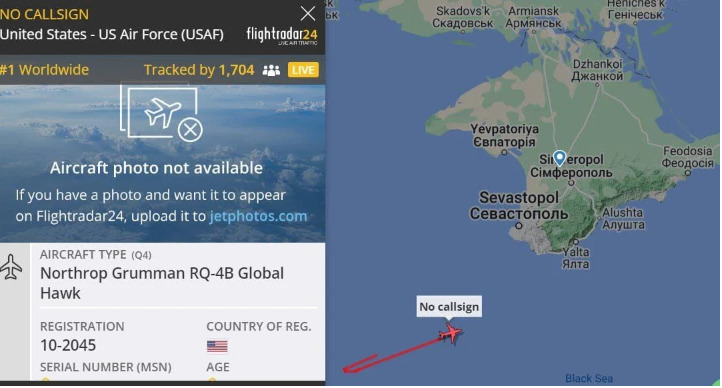
Russians are starting to get tired of US reconnaissance drones near Crimea

Russian observers have long argued that Western countries' reconnaissance drones are often used to gather targeting data for Ukrainian UAV strikes in Crimea, which was annexed by Russia in 2014 and later voted to be part of the country in a referendum. of the same year. RQ 4b long-range drones are used most frequently by the US over the Black Sea, still in international waters, but on the edge of the Russian-claimed airspace above Crimea.
The persistent and formidable intelligence-surveillance-reconnaissance (ISR) assistance from US military assets is increasingly perceived as a provocation to Russia and has spawned a campaign to target it directly to send a message to Washington. Shooting down a drone is not shooting down a manned aircraft, even though it is obviously an incredibly hostile act.
US operators of the drone aim to study Russian air defense processes, including reaction times, radar frequencies and their location with the help of the UAV, Russian defense observers said. While the exact number and composition are unknown, Crimea is heavily defended by Russian long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) systems such as the S-400 and possibly the S-300VM. The S-300VM can strike targets such as short- and medium-range ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, fixed-wing aircraft, parked ECM platforms, and precision-guided munitions. He was transferred to Syria in 2016, at the height of the Donbas War and the Syrian Civil War.

Thanks to our Telegram channel you can stay updated on the publication of new articles from Economic Scenarios.
The article Russians are starting to get tired of US reconnaissance drones near Crimea is from Economic Scenarios .
This is a machine translation of a post published on Scenari Economici at the URL https://scenarieconomici.it/i-russi-incominciano-a-stancarsi-dei-droni-da-ricognizione-usa-vicino-alla-crimea/ on Sun, 22 Jan 2023 14:52:58 +0000.