What is the Tokamak, the nuclear fusion machine
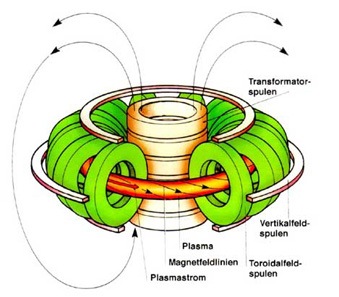
A tokamak is a device used to produce and confine a very high temperature plasma, in order to exploit the energy deriving from controlled nuclear fusion . The name tokamak comes from the Russian acronym for "toroidal chamber with magnetic coils". An acronym that well describes the structure in question.
Plasma is the fourth state of matter, in which atoms are fully ionized, i.e. devoid of the electrons that normally surround them. Plasma is formed by a gas, usually hydrogen or its isotopes (deuterium and tritium), brought to temperatures of millions of degrees, similar to those found at the center of stars.
Under these conditions, the nuclei of atoms can overcome their electrostatic repulsion and fuse together, releasing a large amount of energy. To achieve controlled nuclear fusion, it is necessary to keep the plasma stable and away from the walls of the device, otherwise it will cool down and shut down the reaction.
The tokamak uses a magnetic field generated by powerful electromagnets to confine the plasma into a toroidal (doughnut) shape. The magnetic field has two components: a toroidal one, parallel to the direction of the donut, and a poloidal one, perpendicular to the direction of the donut. The toroidal component serves to keep the plasma from expanding radially towards the walls, while the poloidal component serves to keep the plasma from flowing out the ends of the donut. The poloidal component is obtained by inducing an electric current in the plasma itself, which acts as the secondary winding of a transformer. THE
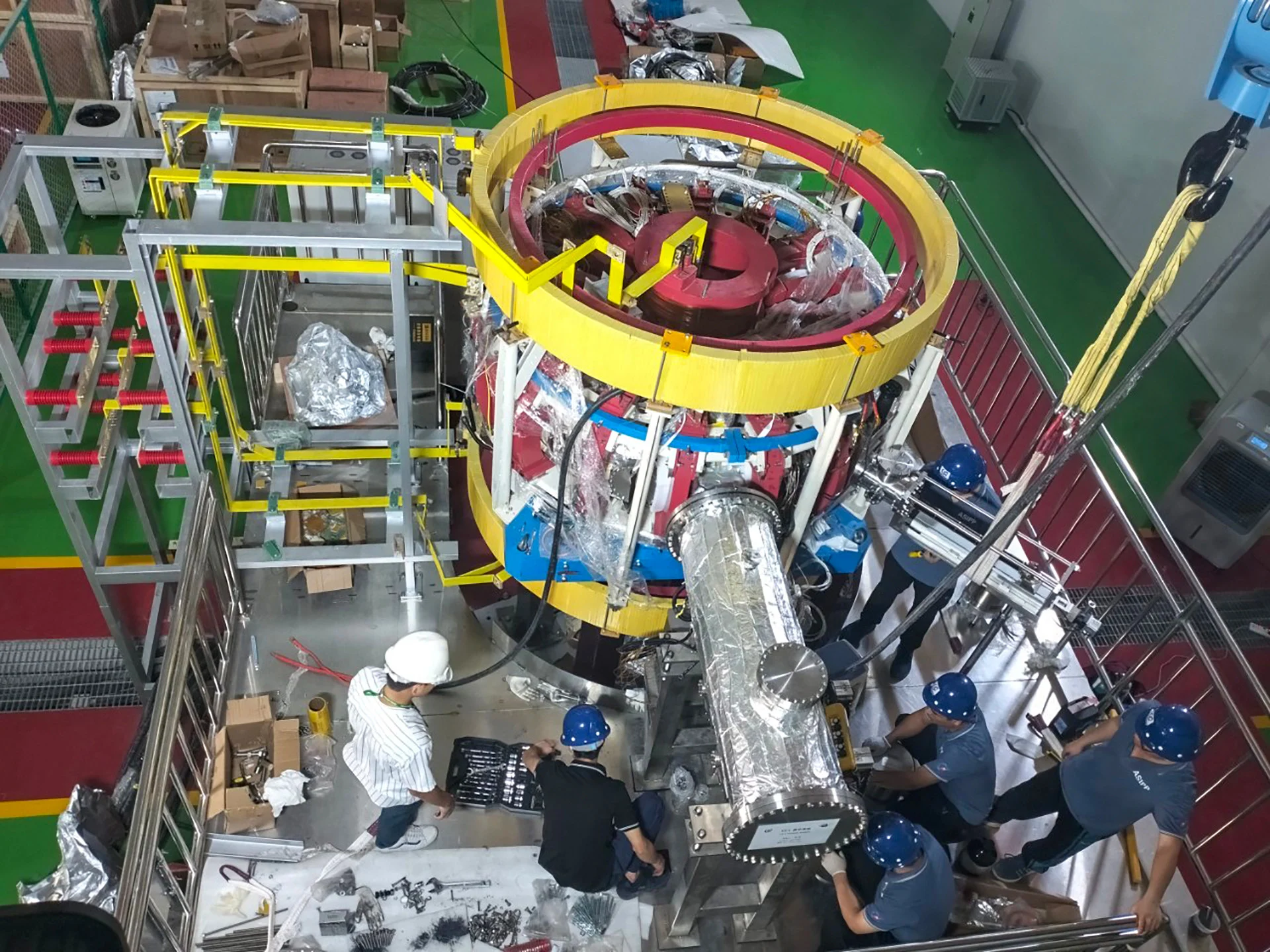
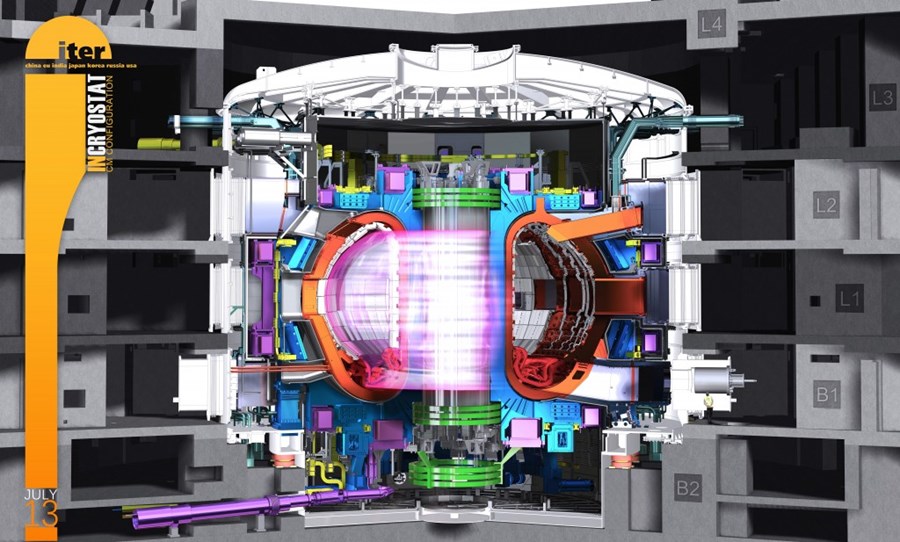
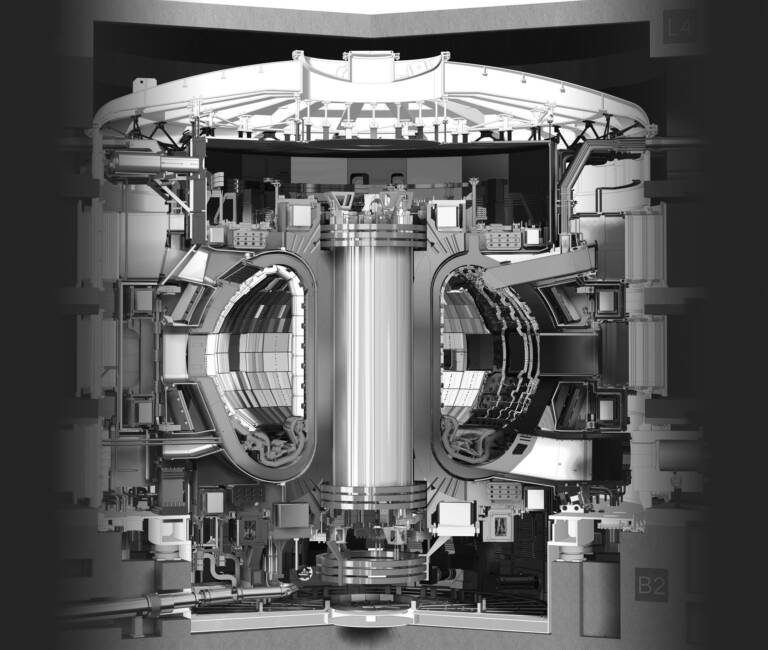
The tokamak therefore has a complex structure, formed by a vacuum chamber in which the plasma is contained, surrounded by copper or superconducting coils which generate the magnetic field, and by various auxiliary systems for heating the plasma, controlling the purity and of gas density, measurement of plasma properties and harvesting of fusion energy. The tokamak is one of the most studied configurations for the construction of a controlled nuclear fusion reactor, as it has been shown to achieve high performance in terms of temperature, density and plasma confinement time.
However, it also presents technical and scientific challenges, such as the need to feed the current into the plasma in a continuous or quasi-continuous way, the management of the instabilities that can compromise the confinement of the plasma, the resistance of the walls to the high temperatures and to the radiations generated from the plasma, and the efficiency in converting thermal energy into electrical energy. Several tokamaks are currently in operation or under construction in various countries of the world, the largest of which is the ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor), located in the south of France.
ITER aims to demonstrate the scientific and technological feasibility of controlled nuclear fusion on an industrial scale, producing more energy than it consumes for operation. Italy participates in the ITER project both as a member of the European Union and with specific contributions, such as the supply of supercables for the electromagnets. ITER has been criticized as a project for its exorbitant cost and excessively long timescales.
Furthermore, Italy hosts one of the most advanced tokamaks in the world, the FTU (Frascati Tokamak Upgrade), at ENEA in Frascati. The purpose of the Italian tokamak is to test different configurations of shapes and materials, in order to develop technological solutions that can be applied in other plants.

Thanks to our Telegram channel you can stay updated on the publication of new articles from Economic Scenarios.
The article What is the Tokamak, the nuclear fusion machine comes from Scenari Economics .
This is a machine translation of a post published on Scenari Economici at the URL https://scenarieconomici.it/cose-il-tokamak-la-macchina-per-la-fusione-nucleare/ on Mon, 28 Aug 2023 05:30:54 +0000.