Are monoclonal and antiviral antibodies effective against the new subvariants? Here’s what Ema says
EMA's Emergency Task Force is not convinced of the efficacy of monoclonal antibodies against the new subvariants. Here's why, what do you think of antivirals and how many of these drugs have been used in Italy so far
The monoclonal antibodies used and available so far against Covid "may not be effective against emerging strains of Sars-CoV-2". To say it is the Emergency Task Force (ETF) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
Our Emergency Task Force warns that monoclonal antibodies may not be effective against emerging strains of SARS-CoV-2. Read the full statement
https://t.co/wBMqYozxiB
#COVID19 #PublicHealth pic.twitter.com/Xi5SEDDwvq— EU Medicines Agency (@EMA_News) December 9, 2022
Currently those authorized by the EMA are Evusheld (tixagevimab/cilgavimab), Regkirona (regdanvimab), Ronapreve (casirivimab/imdevimab) and Xevudy (sotrovimab).
WHY AUTHORIZED MONOCLONALS ARE NOT EFFECTIVE
As explained by the EFT, the monoclonal antibodies authorized so far “are designed to neutralize the virus by binding to the spike protein on its surface. However, emerging strains have mutations in this protein that can reduce the ability of antibodies to bind to it."
Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies (a type of protein) designed to recognize and attach to a specific structure, called an antigen. In this case they are designed to attach to the spike protein, thus preventing the virus from entering the body's cells.
Following the opinion, the experts will then evaluate the possibility of recommending an update of the information for each individual product.
THE MOST RESISTANT SUBVARIANTS
The discovery took place through laboratory tests, from which it emerged that the monoclonal antibodies directed against the spike protein "are poorly effective in neutralizing the Omicron strains BA.4.6 , BA.2.75.2 and XBB". The latter was renamed on social Gryphon and is the recombinant of two sub-lineages of Omicron 2.
Furthermore, reports the EFT, the data show that these monoclonal antibodies "do not significantly neutralize" even the BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 strains (now known as the Cerberus family), which are expected to become dominant in Europe during the next weeks.
WHAT EFT RECOMMENDS
Although it is not yet known from the studies to what extent the neutralizing action is reduced, the task force invites health professionals to "consider alternative treatments, especially if subvariants such as BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 become prevalent".
WHAT ABOUT THE ANTI COVID PILLS?
According to EFT experts, anti-Covid pills such as Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir) and Veklury (remdesivir), which have different mechanisms of action, however, are saved because "they should maintain their activity against emerging strains".
Reason why, reads the note, the body "encourages EU member states to ensure that health professionals have access to these antiviral treatments for patients at high risk of severe Covid-19".
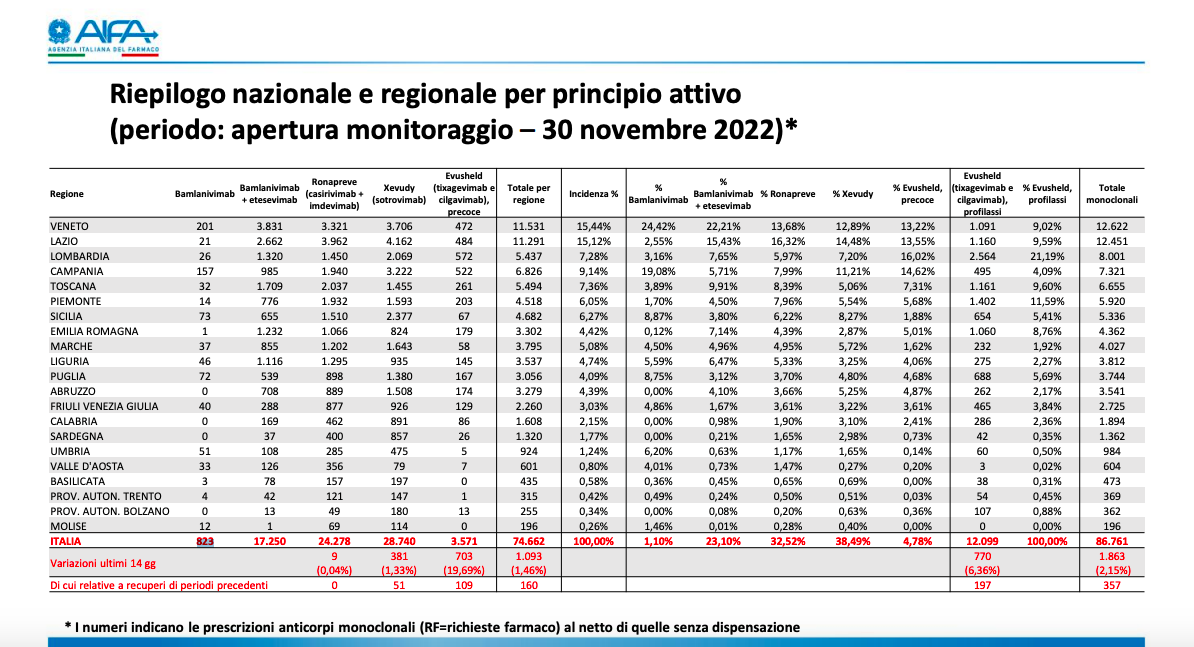
HOW MANY MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES HAS ITALY USED
According to the latest monitoring by the Italian Medicines Agency (Aifa), as of December 1, Italy used 86,761 monoclonal antibodies:
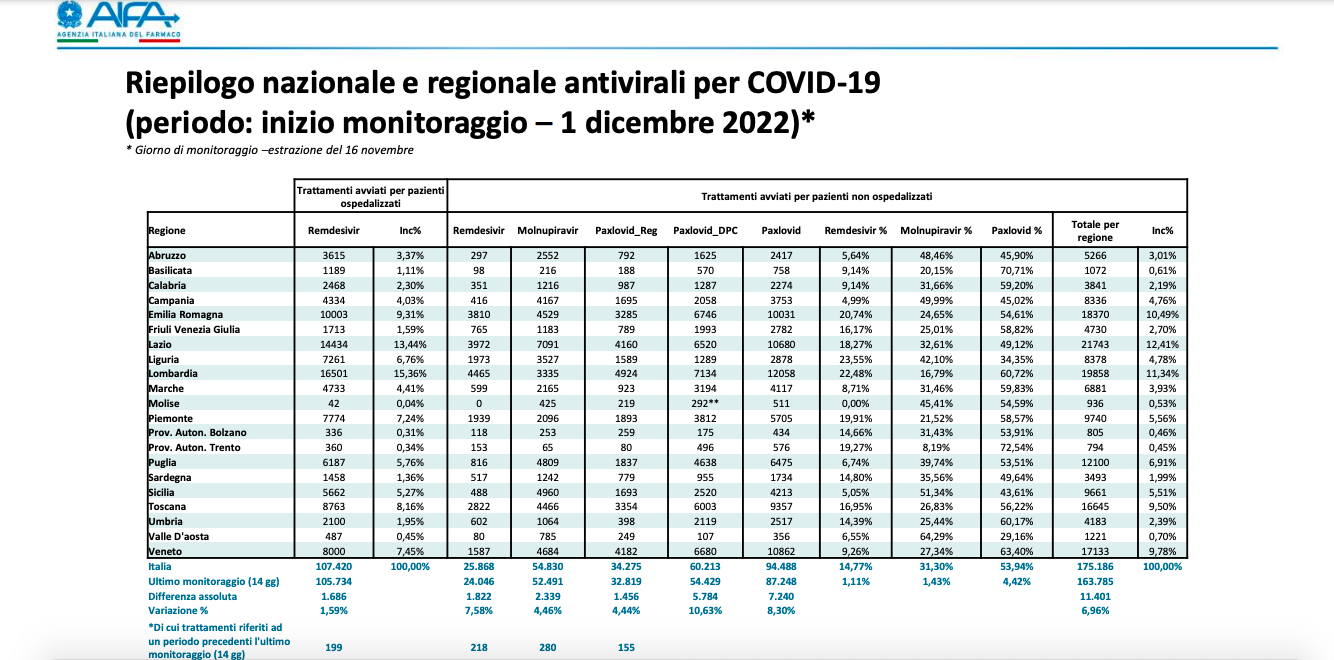
HOW MANY ANTI COVID PILLS HAS ITALY USED
Instead, as regards antivirals, as of 1 December, 107,420 treatments had been started for hospitalized patients, while those started for non-hospitalized patients were 175,186:
This is a machine translation from Italian language of a post published on Start Magazine at the URL https://www.startmag.it/sanita/cosa-ha-detto-ema-efficacia-anticorpi-monoclonali-antivirali-contro-nuove-sottovarianti/ on Tue, 13 Dec 2022 09:47:25 +0000.
