How long will inflation last in Italy and in Europe?

Inflation is expected to be 6.1% in the Eurozone in 2023, to then drop to 2.6% in 2024. The analysis by Michele Morra, Portfolio Manager of Moneyfarm
The latest November inflation data from the Eurozone reminds us that, right now, inflationary pressure remains the main focus for financial markets. Although it seems to have reached a turning point, we are still far from the levels we have been accustomed to in the last decade. The question therefore arises spontaneously: for how much longer can we expect sustained levels of inflation?
Slowing down inflation?
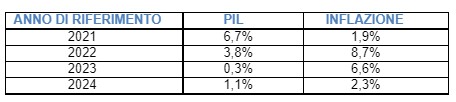
Inflation's grip on the economy should begin to ease during 2023, before settling down definitively in 2024. However, according to the latest data from the EU Commission, inflation will continue to remain high next year: at 7% in European Union and 6.1% in the Euro area. For 2024, on the other hand, a decrease to 3% and 2.6% respectively is expected.
Currently, the sharp rise in inflation is affecting a global economy still grappling with the economic consequences of the pandemic crisis and the war in Ukraine where, in particular, the EU appears to be among the most exposed regions due to its geographical proximity and heavy dependence on Russian fossil fuel imports.
The rush of inflation is also eroding the real value of the additional savings accumulated during the pandemic. Real private consumption growth is therefore projected to slow from 3.7% in 2022 to 0.1% in 2023, before recovering to 1.5% in 2024 as real wages, and hence disposable incomes, they will recover part of the lost purchasing power.
But how did we get to this point? There are several factors that have led to this situation. The main one was the reopening of the post-Covid economy before the supply of goods and services could increase to satisfy the huge excess demand. Added to this are also geopolitical criticalities, such as Russia's invasion of Ukraine, the continuous bottlenecks in the supply chains – a dynamic linked in particular to China and its continuous lockdowns – and the increase in the prices of energy that contributed to the worsening economic situation.
Continuous upward surprises
Inflation in 2022 continued to surprise to the upside. The acceleration and widening of price pressures in the first ten months of the year moved the expected inflation peak to the fourth quarter of 2022 and contributed to raising the annual inflation rate projection to 9.3% in the Union European and 8.5% in the Euro area.
Situation that has negatively affected economic growth and financial markets, so much so that EU and Eurozone countries are expected to experience a technical recession this winter. For 2023, as a whole, real GDP growth is forecast for both the EU and the Eurozone at 0.3%, well below the 1.5% and 1.4% previously estimated.
Focus Italy
According to the latest economic forecasts made by the EU Commission, Italy too will experience an economic slowdown this winter. In fact, it is expected to grow by 0.3% in 2023 and 1.1% in 2024. The inflation rate is expected to rise to 8.7% this year and fall to 2.3% by 2024.
With inflation high and growth weak, it is very likely that consumer spending will stagnate in 2023 and then pick up again in 2024.
This is a machine translation from Italian language of a post published on Start Magazine at the URL https://www.startmag.it/economia/inflazione-italia-europa/ on Sun, 01 Jan 2023 06:19:12 +0000.
