How technology will push medicine beyond its limits

Artificial intelligence, genome editing, 3D printing, smart medicines, virtual and augmented reality. An insight into the main innovations that are accelerating the development of preventive treatments and strategies in the healthcare sector by Gloria Grigolon, Investment Specialist at Pictet Asset Management
The use of technology for health and medical purposes is pushing the limits of medicine, integrating new precision solutions with greater chances of success. Although therapeutic and preventive innovation has improved over the last few years, revolutionizing the healthcare sector, we are now faced with an unprecedented integration of the digital and technological sphere. The definition used by the World Health Organization (WHO) is that of "healthcare boundaries", those limits that innovation will allow to overcome in the near future and which will transform the world of Healthcare.
The huge amount of data available, the use of Artificial Intelligence and latest generation wearable devices are among the innovations that will have the greatest impact not only on the quality of the service offered, but also on the accuracy of clinical studies, on the preventive capacity, on the training of new talents and on accessibility to the basic and specialist healthcare system. Areas of extraordinary interest, on which the Pictet-Health strategy focuses.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
The use of algorithms and machine learning can help identify and diagnose different types of pathologies successfully and in advance (above all, in the oncology field). With reference, for example, to breast cancer, AI already makes it possible to examine the outcome of mammograms 30 times faster than traditional methods and with almost 100% accuracy, reducing the need for biopsies. A deep-learning algorithm could also, in a short time, allow the early diagnosis of lung cancer starting from the AI interpretation of chest radiographs, more advanced than current radiological readings. Artificial Intelligence then has the potential to automate (now manual) analysis processes through the recognition of infection development patterns, making diagnostic tests more effective.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and apps for tracking and monitoring physical activity, will increasingly be able to warn users of any anomalies before their condition becomes critical. Similarly, devices equipped with sensors could prevent falls in older adults by detecting early warning signs such as poor grip strength, low hydration levels or declining muscle mass. The same goes for rehabilitation too, with AI being able to monitor patient progress or adjust treatment plans based on feedback in near real-time.
Taking into consideration the huge amount of data deriving not only from official databases, but also from applications, devices and information transmitted by individual users on a daily basis, Artificial Intelligence will be able to exploit the huge mass of information to make health recommendations and provide constant remote monitoring (for example, for the glucose levels of patients with diabetes), optimizing the dosage and evaluating the effectiveness of the treatments administered.
The evolution of surgical robotics will also allow the execution of ever more precise interventions. Robot-assisted kidney surgery increases the success rate by 52 percent, for example, according to the trade journal ATM. Not only that: robotics can help healthcare workers perform tasks such as warehouse monitoring, disinfecting rooms and transporting medical equipment, freeing up time for healthcare workers.
Finally, new smart devices can offer support to healthcare professionals in activities such as the transcription of clinical data, reducing the technical (and bureaucratic) times of healthcare. Still, enormous progress could be made in the field of home diagnostics. The primary beneficiaries should be "virtual assistants" in the healthcare sector, whose growth estimates stand at 27% CAGR by 2027.
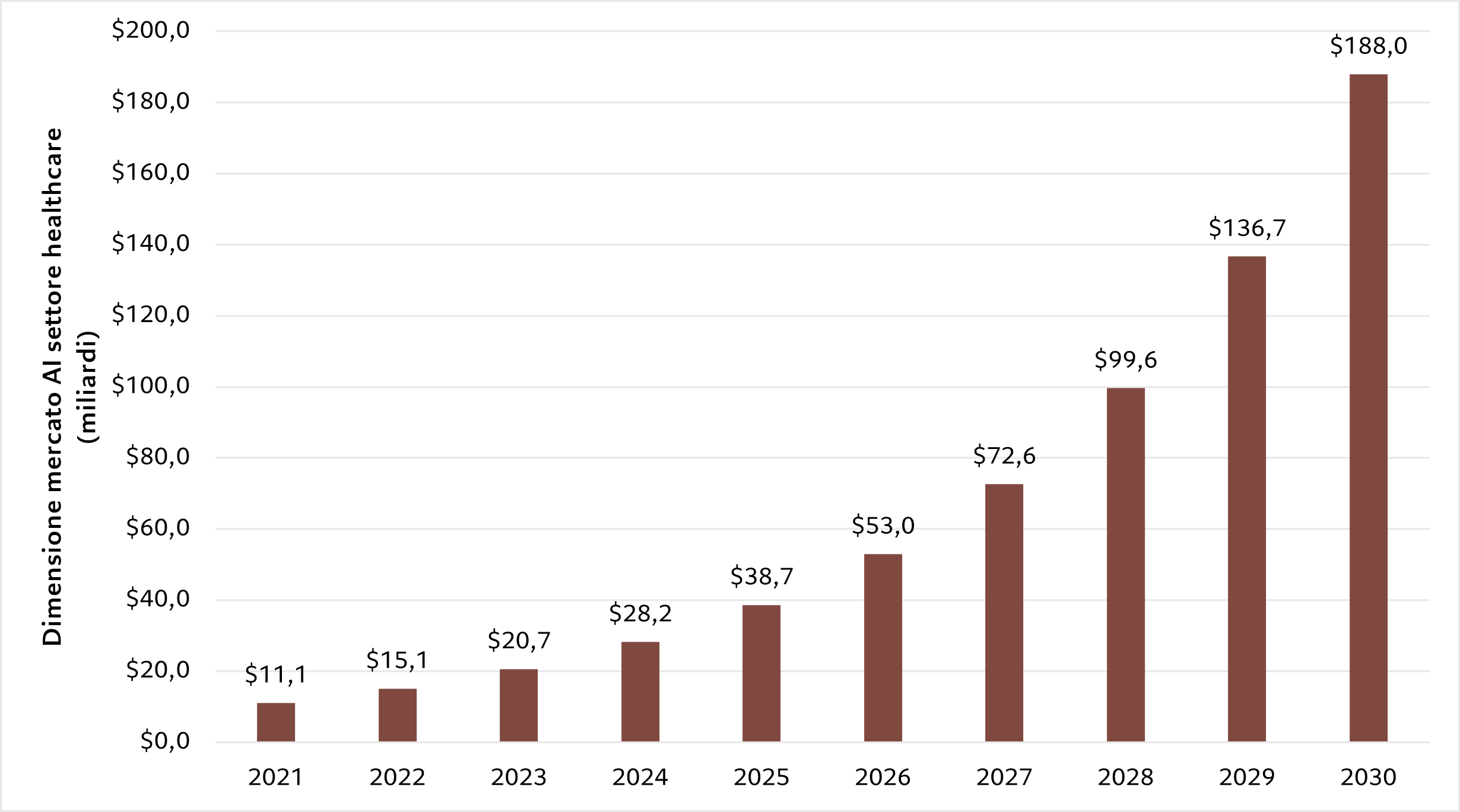
GENOME EDITING (CRISPR)
Genome editing is among the most talked about innovations in the medical field. The activity involves, in fact, the modification of the DNA of living organisms such as plants, animals, but also human beings. While in the plant sector genome editing has the potential to develop, for example, new and better qualities of food, more resistant to external attacks by parasites, its use in the medical sector can help counteract the onset and development of important diseases. In particular, the technology behind the CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) system allows it to act like a sort of scissors, "exploiting the natural mechanisms" of the invading viruses and "cutting" the infected DNA strands.
Human-applied CRISPR editing has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of certain diseases, making significant strides against cancer and HIV within a few years. Not only that: by modifying cellular mutations, CRISPR technology could be able to transform the treatment of rare diseases such as cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia, with a lower impact in terms of costs and effects.
An obstacle to overcome, however, is that which concerns the ethical problems associated with its use: gene editing has in fact the potential to modify genomes at birth, a practice tested in China in 2020 by a group of scientists who claimed to have created the first “design babies” using CRISPR.
3D PRINTING
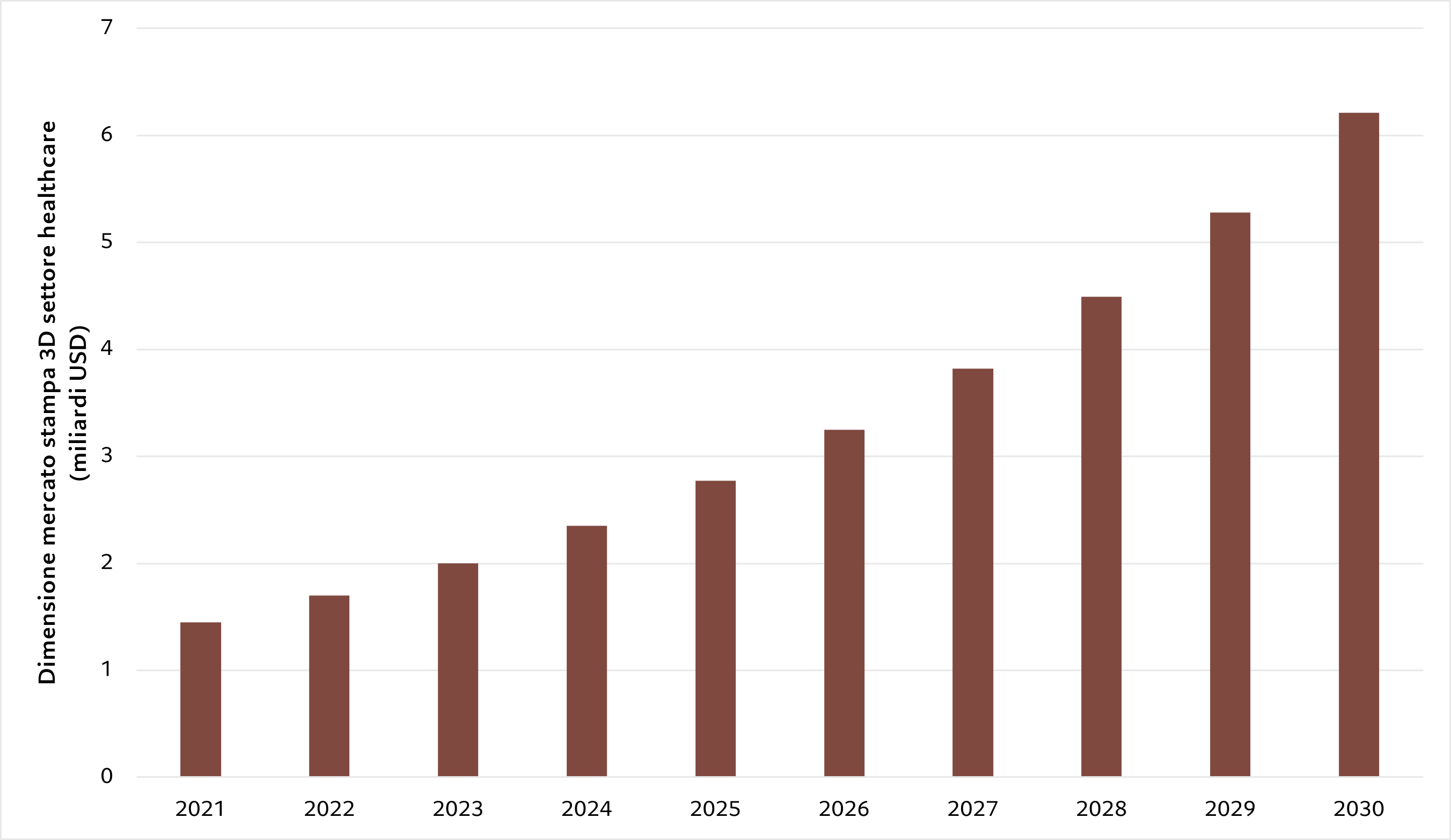
The use of 3D printing techniques in the healthcare sector is growing rapidly. Dental implants, replacement joints, custom-made prostheses and hearing aids are among the main areas of application of this technology, which is gradually specializing in increasingly professional "prints" such as skin tissue and organs. Last but not least, the 3D production of drugs, which will be able to benefit from faster production processes by reducing the cost of products and expanding the audience of potential customers. The use of this technology (according to the American Hospital Association) has already reduced the production time of hearing aids from 7-10 days to one day.
The market size of 3D printing in healthcare was estimated at USD 1.45 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach approximately USD 6.21 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17 .54% in the forecast period 2022-2030.
The growth of public and private investment in medical research and development (R&D) will impact market trends, fostering innovation and the development of advanced solutions, improving healthcare infrastructure and the capacity of institutions to carry out satisfactory activities of R&D.
VIRTUAL AND AUGMENTED REALITY
The virtual reality and augmented reality markets are experiencing full expansion all over the world, especially in the health sector, for the treatment of certain pathologies, but also in support of doctors and surgeons.
In mental health, augmented reality is being used to help patients overcome the fear and anxiety brought on by social interactions. At a neurological level, virtual reality instead allows simulations to be carried out for the treatment of chronic pathologies, helping to make the brain "unlearn" the onset of certain reactions. A research conducted by Forbes reports that in 68% of cases, two hours of exposure to the treatment for fear of heights recorded a reduction in the anxiety of patients subject to vertigo.
In support of surgical activity, augmented and virtual reality have already been tested through the use of helmets to recreate the environment in which surgeons operate, allowing them to immerse themselves in complex clinical situations, observe body and site to operate and creating virtual spaces within which to train. This makes it possible to minimize errors, help the patient in their rehabilitation process and allow students to learn the surgical technique more effectively.
SMART MEDICALS
A group of US researchers from the California Institute of Technology has developed special types of bandages that use sensors to monitor wound healing and administer drugs where necessary.
In particular, this type of medicine exploits electronics, i.e. a thin layer equipped with sensors to detect the temperature or the pH level which can indicate the presence of inflammation or infection, but also the presence of molecules such as uric acid or lactate. By constantly monitoring the wound, the sensors enable localized stimulation to be activated, if necessary, to accelerate tissue closure.
This particular type of bandage should (according to the team's notes) "promote faster closure of wounds, increase blood flow to injured tissues and improve skin recovery by significantly reducing scar formation". This is a technology that could primarily benefit those with depressed immune systems, burns or diseases such as diabetes, often related to slow healing. The main obstacle to the use of this new technology at the moment is represented by the high costs, but also by the still scarce collection of data.
This is a machine translation from Italian language of a post published on Start Magazine at the URL https://www.startmag.it/sanita/come-la-tecnologia-fara-superare-alla-medicina-i-suoi-limiti/ on Sun, 23 Apr 2023 05:09:13 +0000.
