The critical and strategic dependencies of Italian industry. Confindustria report

There are 333 critical products, for which the industry is permanently vulnerable in recent years. What the report of the Confindustria Study Center says
Overall, Italy's critical dependencies thus defined are around 16% of total imports in value in the period 2012-2021 (approximately 29 billion euros out of 187 on average per year) and around 7% as a variety of products compared to all imported types (370 products out of 5,042). In particular, in order to characterize the critical supplies for the Italian industry, in the third step only the goods intended for businesses (intermediate and investment) are considered, excluding those for consumption, and the products that are critical in most of the last years (Figure C).
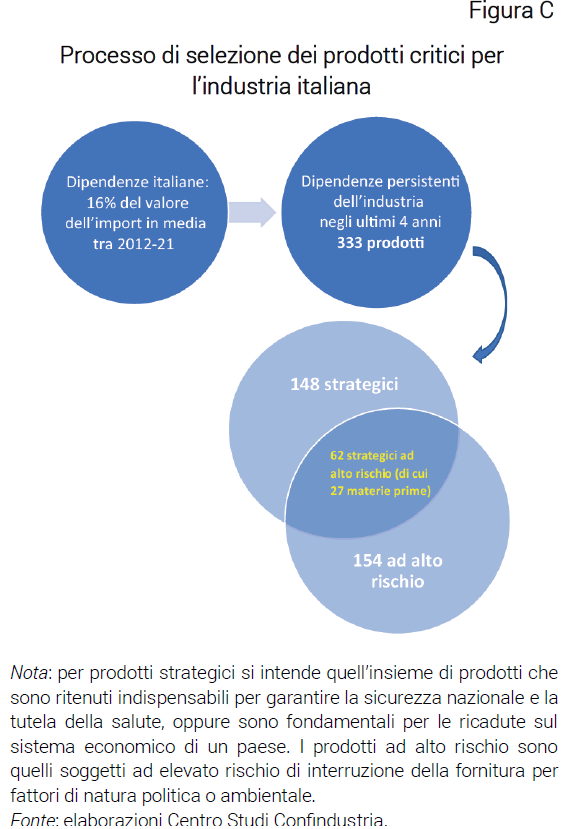
The set of critical supplies to industry, thus defined, represents on average around 9% of the value of Italian imports (17 billion euros) and around 7% as the number of different types of imported products (333) between 2018 and 2021.
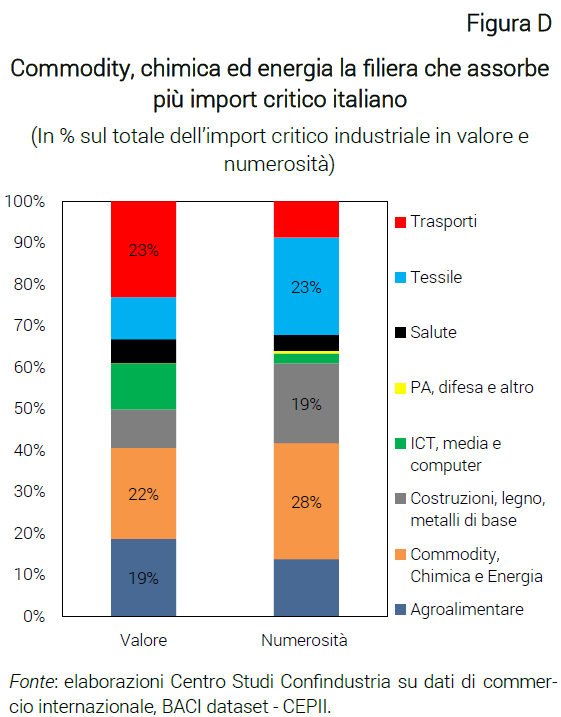
These products are concentrated, in value, in the transport chain (23% of the total of critical products, especially the production of iron and steel; Figure D), of which however there are relatively few product varieties (only 9% of the total number ), and in the commodity, chemical and energy supply chain (22% of critical products, mainly basic chemicals). This is followed by the agro-food and ICT chain (computers and peripherals, components and electronic boards), with shares around 15-18%, and that of construction and base metals and textiles, with shares in value around 10%. In the textile sector, in particular, there are numerous types of critical products, 23%, but in small quantities or on average inexpensive. Lastly, the health supply chain represents 5% of the total value of critical imports.
Italian industry depends on Chinese supplies
Among the countries of origin of the critical imports of the industry, the centrality of China stands out, which represents the first supplier for about 23% of the products, in terms of number of different types, which are worth over 25% of the value of the critical imports, almost 3.4 billion euros a year on average between 2018 and 2021. The United States follows at a distance, the first supplier of 10% of the total variety of critical products, which however are worth only 6% of the total, l 'India and Turkey (about 8-10% of products), Ukraine and Switzerland (1-4% of varieties, but between 9 and 11% in value).
What dependencies on China and the United States?
The vulnerability of Italian industry from China is concentrated, in value, in ICT products, for about 47% of the value of critical imports for which China is the first supplier; these are few products (only 2% as a total variety), which consist in particular of products used in the manufacture of computers and chemicals used in photography. In terms of number, on the other hand, textile products excel (31% of the total types, 18% in value), which are instead highly differentiated. The other relevant supply chains concern transport (16% in value, 11% in variety) and construction, wood and base metals (14% in value).
Of the total value of critical imports for which the USA is the first supplier, however, 44% are health products (which, however, account for only 6% in terms of number of products; these are above all hormones, especially insulin), and about 31% in the commodity chain (which are first in terms of variety, 47% of the total) and in the construction chain.
Which products are strategic?
Among the vulnerable products, strategic ones can be isolated, i.e. that set of products which are considered indispensable for guaranteeing national security and the protection of health, or are fundamental for the repercussions on the country's economic system. In particular, it includes those intermediate or capital goods that are crucial for the realization of the energy and digital transitions, which in turn strengthen the competitive capacity (which must be eco-sustainable) of industry and services.
To include as many potential strategic products as possible in the analysis and to consider not only raw materials but also semi-finished products and capital goods, and therefore the entire value chain, in a holistic vision that allows for the identification of strategic dependencies also of a technological nature, various institutional sources are used which have compiled a list of strategic products: the European Commission, the International Trade Administration (ITA, an agency of the US Department of Commerce which promotes exports of US goods and services not agriculture) and the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
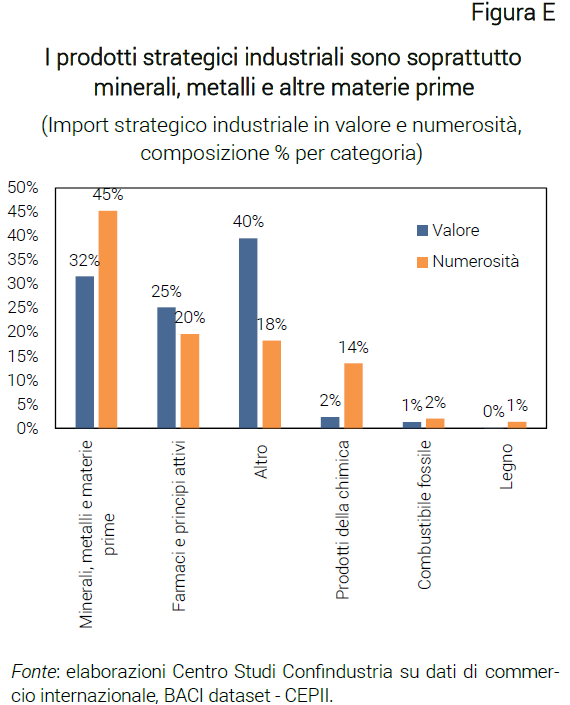
From the union of the products identified by these three sources, we identify for Italy 148 strategic products of the 333 critical ones, i.e. about 44% of the varieties and about 61% of the value of all critical products, classifiable as follows: minerals, metals and other critical raw materials; drugs and active ingredients; chemical products; fossil fuels; wood; other (not classifiable in the previous categories).
The most numerous category with a high aggregate value is that of minerals, metals and other critical raw materials (45% in quantity, 32% in value) mainly used in the production of iron and steel, followed by pharmaceuticals and active ingredients ( 20%, equal to 25% in value) and by other strategic products (which are 18% of the varieties but are worth 40%), mainly involved in the production of computers and peripheral equipment, in the construction of ships and floating structures and in the paper and cardboard manufacturing (Figure E). On the other hand, the share represented by chemical products is smaller, which in any case represents 14% of all types of critical products (2% in value), and by fossil fuels and wood (which fluctuate between 0 and 2%).
As supply chains, those most affected by the presence of strategic products compared to the total import of critical products are, in order of importance, those of health, ICT (over 90% in value but around 50% in variety), commodities and transport (about 85% in value and between 60-80% in variety) and construction (over 60% in both value and variety). Conversely, the textile and defense supply chains are not involved.
Taking into consideration the main suppliers of all critical products, the value of imports from Russia, Switzerland and Brazil can be considered strategic shares exceeding 90%. As a variety, however, only Switzerland and Russia retain strategic prevalence. The shares in value are also very high for Japan, Ukraine, China and the United States, which all exceed 60%, remaining on about half in value, while the remaining countries have strategic shares between 15% and 45% in value and around 30% as a variety, except Canada.
In terms of shares on total strategic imports, two other nations deserve to be mentioned: the United Arab Emirates, from which all critical imports can be considered strategic and represent 8% of the total value of strategic imports, and the United United Kingdom, of which 85% of critical imports in variety can be considered strategic, which represents, by number of products, 6% of all strategic imports.
Critical and strategic raw materials
Among the various classifications of strategic products, that of Minerals, metals or other critical raw materials deserves particular attention, since various policy efforts go in the direction of alleviating dependencies precisely in this area.
In particular, the Critical Raw Materials Act presented in mid-March 2023 by the European Commission provides for a series of actions "to ensure the EU's access to a secure, diversified, accessible and sustainable supply of essential raw materials", essential to achieve the set goals in the climate and digital fields by mitigating the risks for supply chains linked to these strategic dependencies.
Among the 148 strategic products, 67 are raw materials (45%), and are worth as much as 32% of strategic imports. These are minerals (20 products), metals (18), chemicals (16) and ferrous metals (13). In value, the products that matter most are products related to the production of iron and steel (almost 80%) while in terms of variety they account for about 20%, however very close to the two most numerous categories of basic chemical products and metals base precious and other non-ferrous metals.
This is a machine translation from Italian language of a post published on Start Magazine at the URL https://www.startmag.it/economia/vulnerabilita-industria-italiana-prodotti-critici/ on Tue, 15 Aug 2023 05:42:40 +0000.
