Turkey earthquake, what happens to the Earth?
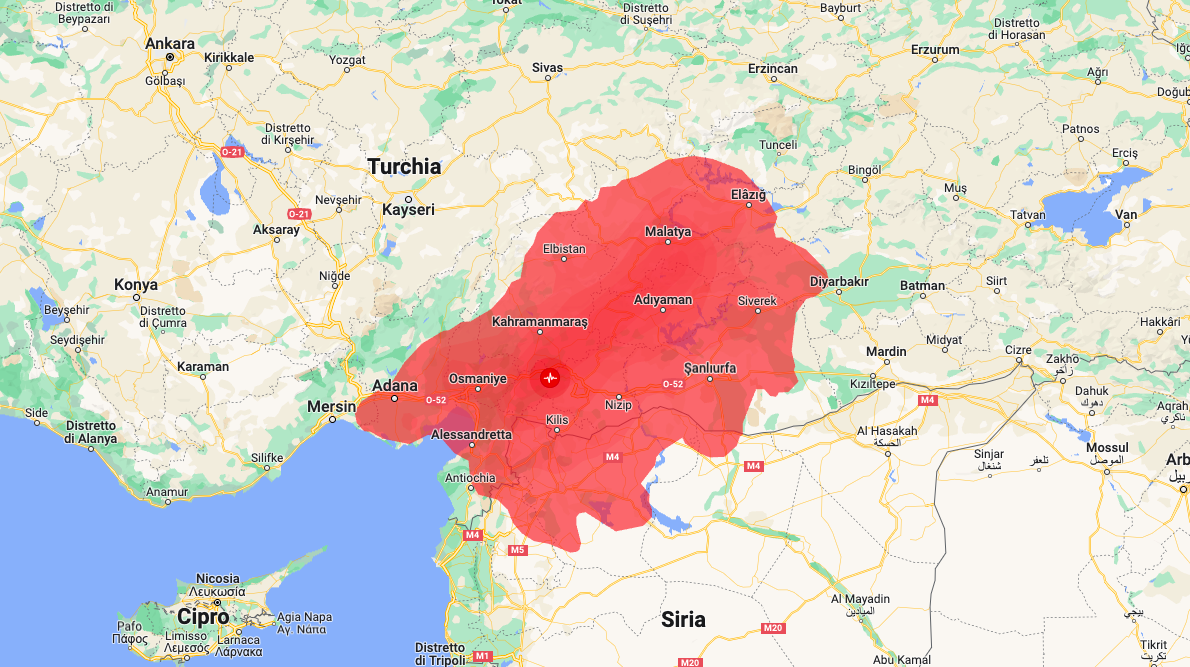
The earthquake in southern Turkey, near the border with Syria, was caused by a horizontal slip of about 3 meters of the Anatolian plate with respect to the Arabian plate, activating the East Anatolian fault for at least 150 kilometers. Expert analysis, commentary and predictions
Like 130 nuclear bombs. This is the magnitude of the earthquake that occurred in Kahramanmaras in southern Turkey near the border with Syria , according to Turkish engineer and geophysicist Övgün Ahmet Ercan reported by the Hurriyet website .
For some experts it was two separate earthquakes that occurred very close in time and space, for others, however, the second was an aftershock of the first.
Here's what happened in Turkey.
THE TWO SHOCKS
After the 7.8 magnitude quake with its epicenter near Gaziantep that occurred in the night between Sunday and Monday, a new 7.5 magnitude earthquake struck Elbistan late yesterday morning, about 100 kilometers away. The first quake, seismologist Alessandro Amato of the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (Ingv) told Ansa , was 1,000 times stronger than the one that hit Amatrice in 2016 and 30 times stronger than that of Amatrice. 'Irpinia of 1980.
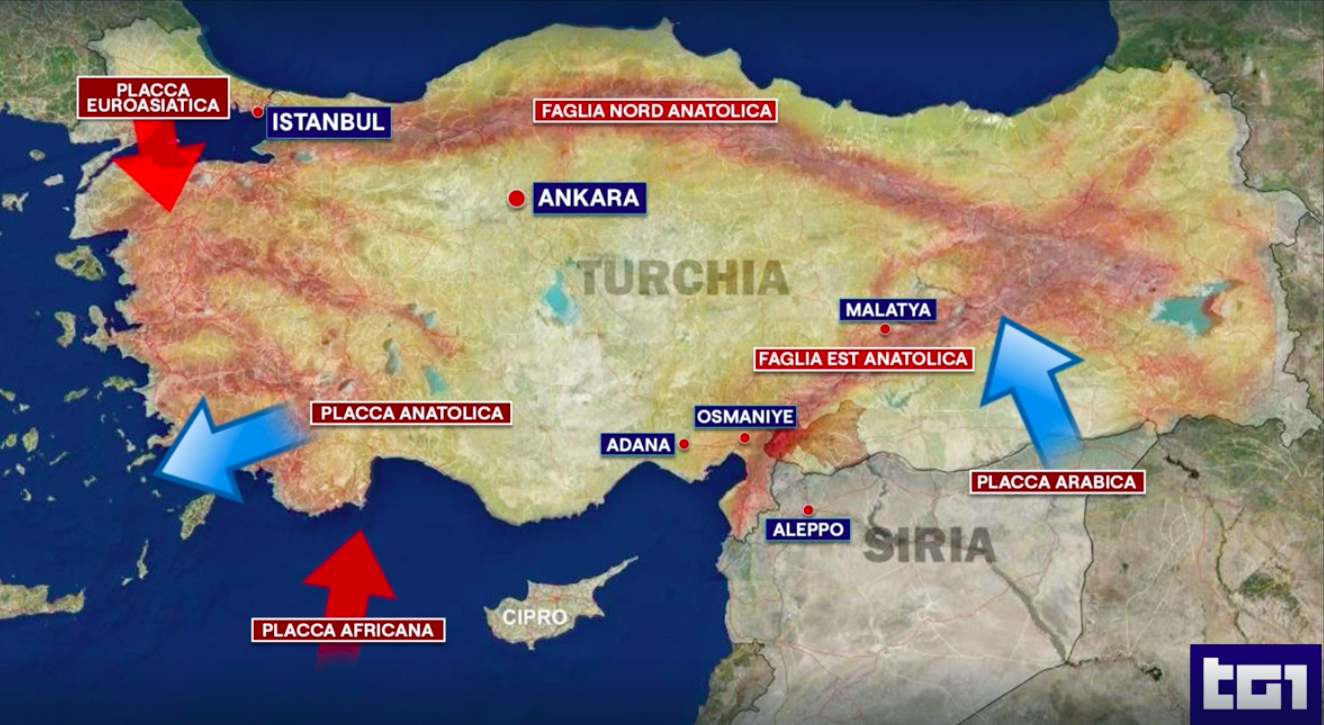
"The earthquake occurred on the East Anatolian fault, at the triple point where the Anatolian, Arabian and African blocks converge," he added.
The fault, according to the expert, "probably came to deform the coast".
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF THE EARTHQUAKE: NATURE…
It was therefore the East Anatolian fault, one of the two major faults present in Turkey, that triggered the first strong shock which was followed and will be followed by many others. This, explained Carlo Doglioni, president of Ingv, is "one of the most active in the Middle East, together with that of the Dead Sea which crosses Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan and which separates the Arab plate from the African one".
In an interview with Corriere della Sera he specified that "there has been a horizontal sliding, therefore on the same level, of the Anatolian plate towards the Southwest with respect to the Arabic plate".
The phenomenon “has generated a type of fault that seismologists call 'shallow depth transcurrent' with a hypocentre, ie the deep place where it unleashes itself, between 15 and 20 kilometres. In other words, Turkey in the estimates has actually slipped by 5-6 meters compared to Syria”. However, more precise data will be available in the next few days from ESA's Sentinel and ASI's CosmoSkymed satellites.
… AND THE MAN
But in addition to the unpredictability of the nature against which it is not possible to intervene, according to an expert reported by Ansa , "perhaps if this earthquake had occurred in a more developed country, where there are stricter building regulations, such as in Japan for example, which has many large earthquakes, the damage would have been much less widespread.”
"I think – he continued – that some buildings would have collapsed anyway, it is common in most earthquakes, but we would not have had such widespread devastation and a large number of collapsed buildings, as we have seen in Turkey".
In this regard, Doglioni observed that "in 2012 the Turkish government passed a law to start a renewal of the building stock, but it will take years before it can produce effects".
WHY THERE
According to what was declared by the Ingv seismologists, "Turkey is located in a highly seismic area crossed by numerous fault systems: the area affected by the earthquake [on Sunday night, ed . ] is considered to have a very high seismic hazard".
Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan said this was the biggest disaster recorded in the country since 1939, when the Erzincan earthquake (7.8 on the Richter scale) killed 33,000 people. More recently we recall the one in 1999 in Izmit (7.6 on the Richter scale) which caused 17,000 deaths.
What happened on Sunday night is not only seismologically significant for Turkey but globally as well: “There has never been an earthquake of this size here since we have installed seismometers all over the world for monitoring, since about 1900,” he said the expert quoted by Ansa .
TSUNAMI RISK
Scholars also wondered about the possibility of a tsunami as a result of such an event because, as Amato observed, it was "by far the strongest event to have activated the Tsunami Warning System since it existed".
Seismographs from all over the world recorded it and, as regards the tsunami warning, the second event to have activated the system was that of Samos in 2020, of magnitude 7.0.
WHAT WILL HAPPEN NOW
“We can safely say that there will be tens of thousands, if not hundreds of thousands, of aftershocks. We hope that most will be of low intensity and will not cause damage but there is still the possibility that there are strong ones,” said the expert quoted by Ansa .
This is a machine translation from Italian language of a post published on Start Magazine at the URL https://www.startmag.it/mondo/terremoto-turchia-cosa-succede-alla-terra/ on Tue, 07 Feb 2023 09:29:57 +0000.
