Will Russia leave Germany without gas?

Russia has heavily cut gas flows through Nord Stream 1, and Germany fears running out of fuel for homes and businesses. Here are data, forecasts and comparisons with Italy
Last week Russia reduced the natural gas supplies passing through Nord Stream 1 by 60 percent: it is the pipeline that reaches Germany and one of the most important energy infrastructures for Europe, which depends on Moscow for the most part. part of imports of this fuel.
Dependence is very high in Germany, the largest economy in the Union. Last Thursday, in fact, the German government activated phase two (of three) of the emergency plan to prepare for the possibility of a total blockade of flows from Russia, which would have very negative consequences for industrial activity.
WHAT GERMANY RISKS
The experts of the administration of Chancellor Olaf Scholz – Bloomberg reports – have developed various risk scenarios, and in none of these the country will have enough gas for the winter months. Klaus Mueller, head of BNetzA, the regulator of the German gas network, said that "if we have a very, very cold winter, if we are careless and too generous with gas, then it will not be nice".
In practice, Germany risks not being able to guarantee heating to its population, having to impose the closure of factories due to lack of energy and, more generally, risks an economic recession. The crisis can be mitigated by resorting to fuels other than gas but more polluting – that is, coal -, while the transition to renewable sources will take years to become a reality.
EXODUS OF MANUFACTURING?
Energy-intensive companies – those that consume large amounts of energy, such as those of steel or paper – may be forced to reduce production or stop it altogether. In this way, domestic heating would perhaps be guaranteed more easily, but the general economic situation would suffer. Also because some systems need to be fed constantly, or they risk breaking.
Looking ahead, moreover, the lack of abundant and low-cost energy – such as Russian gas was – could induce manufacturing companies to leave Germany to move elsewhere.
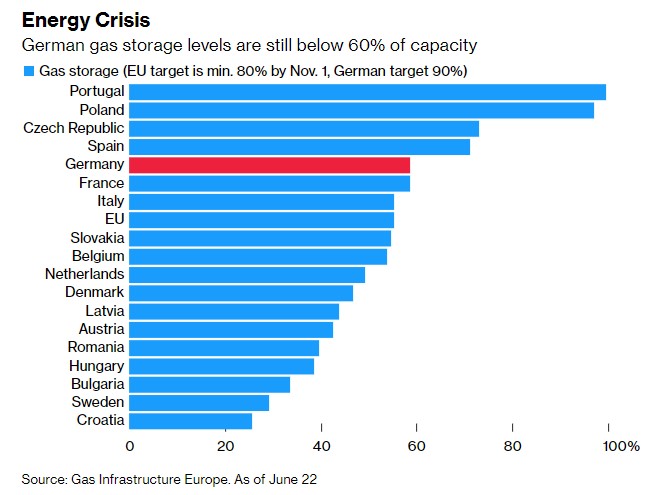
THE QUESTION OF STORAGE
The German government wants to fill its gas reserves to 90 percent by November. According to the latest forecasts, it will take at least 115 days to reach the target, provided that gas flows remain at current volumes. It does not seem likely, however, as the Kremlin is taking an increasingly aggressive posture towards Europe and could further limit energy supplies in retaliation for sanctions imposed after the invasion of Ukraine. Furthermore, in July Nord Stream 1 will be closed for maintenance work: the German government fears that Russia may decide not to reactivate it.
If the situation worsens, Germany could activate phase three of its emergency plan and begin rationing gas. Energy company Uniper, the country's main importer of Russian gas, has already said it may have difficulty complying with supply contracts with its customers (power companies and manufacturing firms) should Moscow continue to push ahead with the cuts. to gas exports.
THE ESTIMATES OF THE BUNDESBANK
According to estimates by the Bundesbank, the German central bank, in 2023 Germany's economy will contract by more than 3 percent if Russia cuts off gas flows.
Some companies are already gearing up to tackle the crisis in energy supplies and prices: the chemical company BASF could decrease production levels, while the car manufacturer BMW could power its buildings not with gas but with electricity. The German division of pharmaceutical group Roche Holding said instead it could replace some of the gas with oil, although it is a much less efficient fuel. Citizens, on the other hand, could find themselves paying much more expensive bills.
WHAT THE ECB BULLETIN SAYS
The latest Economic Bulletin of the European Central Bank states that "among the major euro area countries, Germany and Italy have the highest level of dependence on Russian gas", both with shares exceeding 40 percent compared to total imports.
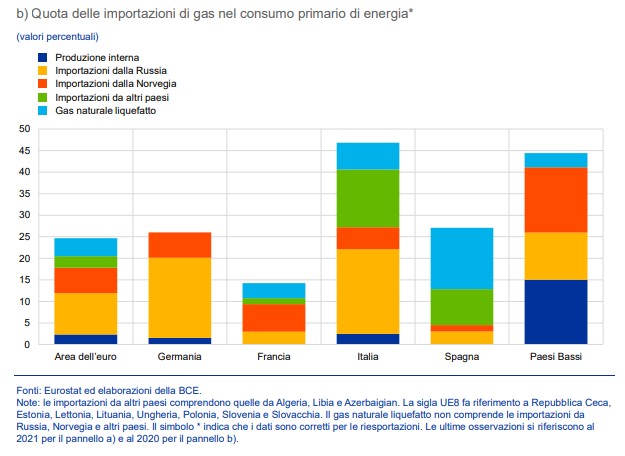
HOW MUCH ITALY RISKS
According to a recent survey by the Confindustria Study Center , "the incidence of energy costs on total production costs for the Italian economy is estimated to reach 8.8% in 2022, more than double the corresponding French figure (3 , 9%) and almost a third more than the German one (6.8%) ”. The risk is that "Italy's cost competitiveness gap from the main European partners" will increase.
For Italy, the rise in the price of energy translates into "an estimated growth in the energy bill of between 5.7 and 6.8 billion on a monthly basis". For Germany, on the other hand, the increase "is estimated between 7.7 and 8.0 billion per month for the total economy […] while for France the estimates are between 1.7 and 1.8 billion per month (20, 2 – 21.8 per year) for the total economy ".
The Italian vulnerability is due to the fact that gas is widely used not only as a source of electricity production, but also as a fuel in production processes. Its rise is therefore the main reason for the greater impact of the energy crisis on production costs compared to France and Germany.
This is a machine translation from Italian language of a post published on Start Magazine at the URL https://www.startmag.it/energia/germania-gas-russia-crisi/ on Mon, 27 Jun 2022 13:52:53 +0000.
